The official KVS PGT Maths Syllabus 2025 has been released on the Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS) website. This syllabus is designed to evaluate the key competencies needed to teach Mathematics at the senior secondary level in Kendriya Vidyalayas. Having a thorough understanding of the syllabus helps candidates focus on relevant topics, plan their preparation effectively, and improve their chances of success in the exam.
Table of Contents
KVS PGT Mathematics Syllabus 2025 – Overview
The KVS PGT Mathematics Syllabus 2025 has been released by Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS) to evaluate candidates’ subject expertise and teaching aptitude for the Post Graduate Teacher (Mathematics) position. The syllabus focuses on advanced mathematical concepts as well as communication, reasoning, and classroom skills necessary for teaching at the senior secondary level.
Key Subjects Covered
The Mathematics section includes topics from:
- Algebra
- Calculus
- Geometry
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Statistics
- Other key senior secondary level concepts
Apart from Mathematics, the exam also includes:
- Language Proficiency (English & Hindi): Grammar, comprehension, vocabulary, writing skills
- Teaching Aptitude: Pedagogical skills, communication, classroom management
- General Awareness, Reasoning, and Computer Literacy
This comprehensive structure ensures candidates are thoroughly assessed in both subject matter and teaching skills.
KVS PGT Mathematics Exam Pattern 2025
The KVS PGT Mathematics Exam Pattern 2025 is structured to assess candidates through an objective-type format. The exam consists of four sections with a total of 180 multiple-choice questions (MCQs), each carrying 1 mark, resulting in a total of 180 marks. The duration of the exam is 3 hours (180 minutes). It is conducted in a bilingual format (English and Hindi).
Section-wise Distribution:
| Part | Subjects | No. of Questions | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part I | General English | 10 | 10 |
| General Hindi | 10 | 10 | |
| Part II | General Awareness & Current Affairs | 10 | 10 |
| Reasoning Ability | 5 | 5 | |
| Computer Literacy | 5 | 5 | |
| Part III | Perspectives on Education and Leadership | 40 | 40 |
| Part IV | Subject Concerned – Mathematics | 100 | 100 |
| Total | – | 180 | 180 |
This detailed structure ensures that candidates are tested not only on their mathematical knowledge but also on their overall aptitude and readiness for a teaching role in Kendriya Vidyalayas.
Detailed KVS PGT Maths Syllabus 2025
Subject specific syllabus includes the concepts of NCERT/CBSE syllabus and Text Books (Classes XI & XII), however, the questions will be testing the depth of understanding and application of these concepts at the level of Post- Graduation.
Sets
Sets and their representations, Empty set, Finite and Infinite sets, Equal sets, Subsets. Subsets of a set of real numbers especially intervals (with notations). Universal set. Venn diagrams. Union and Intersection of sets. Difference of sets. Complement of a set. Properties of Complement.
Relations & Functions
Ordered pairs. Cartesian product of sets. Number of elements in the Cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the set of reals with itself (upto R x R x R). Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain, co-domain and range of a relation. Function as a special type of relation. Pictorial representation of a function, domain, co-domain and range of a function. Real valued functions, domain and range of these functions, constant, identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum, exponential, logarithmic and greatest integer functions, with their graphs. Sum, difference, product and quotients of functions.
Trigonometric Functions
Positive and negative angles. Measuring angles in radians and in degrees and conversion from one measure to another. Definition of trigonometric functions with the help of unit circle. Truth of the identity sin²x + cos²x = 1, for all x. Signs of trigonometric functions. Domain and range of trigonometric functions and their graphs. Expressing sin(x±y) and cos(x±y) in terms of sinx, siny, cosx & cosy and their simple applications. Identities related to sin2x, cos2x, tan2x, sin3x, cos3x and tan3x.
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Need for complex numbers, especially √−1, to be motivated by inability to solve some of the quadratic equations. Algebraic properties of complex numbers. Argand plane
Linear Inequalities
Linear inequalities. Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in one variable and their representation on the number line.
Permutations and Combinations
Fundamental principle of counting. Factorial n (n!). Permutations and combinations, derivation of Formulae for nPr and nCr and their connections, simple applications.
Binomial Theorem
Historical perspective, statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral indices. Pascal’s triangle, simple applications.
Sequence and Series
Sequence and Series. Arithmetic Progression (A.P.). Arithmetic Mean (A.M.) Geometric Progression (G.P.), general term of a G.P., sum of n terms of a G.P., infinite G.P. and its sum, geometric mean (G.M.), relation between A.M. and G.M.
Straight Lines
Slope of a line and angle between two lines. Various forms of equations of a line: parallel to axis, point-slope form, slope-intercept form. Distance of a point from a line.
Conic Sections
Sections of a cone: circles, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola, a point, a straight line and a pair of intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a conic section. Standard equations and simple properties of parabola, ellipse and hyperbola. Standard equation of a circle.
Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in three dimensions. Coordinates of a point. Distance between two points.
Limits and Derivatives
Derivative introduced as rate of change both as that of distance function and geometrically. Intuitive idea of limit. Limits of polynomials and rational functions, trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions. Definition of derivative, relate it to scope of tangent of the curve, derivative of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric functions.
Statistics
Measures of Dispersion: Range, Mean deviation, variance and standard deviation of ungrouped/grouped data.
Probability
Random experiments; outcomes, sample spaces (set representation). Events; occurrence of events, ‘not’, ‘and’ and ‘or’ events, exhaustive events, mutually exclusive events, Axiomatic (set theoretic) probability, connections with other theories of earlier classes. Probability of an event, probability of ‘not’, ‘and’ and ‘or’ events.
Relations and Functions
Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.
Matrices
Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero and identity matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Operation on matrices: Addition and multiplication and multiplication with a scalar. Simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. On commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order 2). Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries).
Determinants
Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), minors, co-factors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
Continuity and Differentiability
Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivative of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions. Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives.
Applications of Derivatives
Applications of derivatives: rate of change of bodies, increasing/decreasing functions, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real-life situations).
Integrals
Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts. Evaluation of simple integrals of the following types and problems based on them.
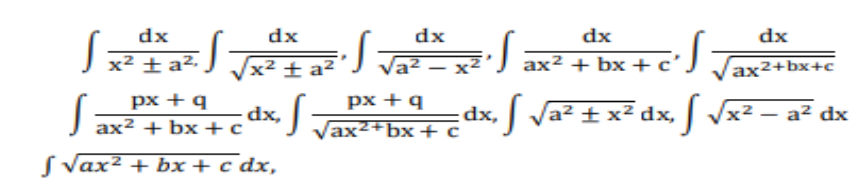
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Basic Properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
Applications of the Integrals
Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, circles/parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only)
Differential Equations
Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, solutions of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type: dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are functions of x or constants. dx/dy + px = q, where p and q are functions of y or constants.
Vectors
Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Definition, Geometrical Interpretation, properties and application of scalar (dot) product of vectors, vector (cross) product of vectors.
Three-dimensional Geometry
Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Angle between two lines.
Linear Programming
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions (bounded or unbounded), feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints).
Probability (Advanced)
Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability, independent events, total probability, Bayes’ theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution, mean of random variable.
Detailed KVS PGT Maths Syllabus 2025 in Hindi
समुच्चय
समुच्चय और उनके निरूपण, रिक्त समुच्चय, सीमित और असीमित समुच्चय, सम समुच्चय, उप समुच्चय। वास्तविक संख्याओं के सेट के उप समुच्चय, विशेष रूप से इंटरवल्स (सांकेतिक रूप में)। यूनिवर्सल सेट। वेन आरेख। सेट्स का संयोजन और छेदन। समुच्चय का अंतर। किसी समुच्चय का पूरक। पूरक के गुण।
संबंध एवं फलन
क्रमबद्ध युग्म। समुच्चय का कार्तीय गुणनफल। दो सीमित समुच्चय के कार्तीय गुणनफल में तत्वों की संख्या। वास्तविक संख्याओं के समुच्चय का अपने आप से कार्तीय गुणनफल (R x R x R तक)। संबंध की परिभाषा, चित्रात्मक आरेख, डोमेन, को-डोमेन और रेंज। फलन को एक विशेष प्रकार के संबंध के रूप में समझना। फलन का चित्रात्मक निरूपण, डोमेन, को-डोमेन और रेंज। वास्तविक मान वाले फलन—स्थिर, पहचान, बहुपद, घातांक, लॉगरिदमिक, रैशनल, साइनम, गुणनफल आदि के ग्राफ। फलनों का योग, अंतर, गुणन और भाजक।
त्रिकोणमितीय फलन
धनात्मक और ऋणात्मक कोण। रेडियन और डिग्री में कोण मापन एवं एक से दूसरे में परिवर्तन। यूनिट सर्कल की सहायता से त्रिकोणमितीय फलनों की परिभाषा। पहचान sin²x + cos²x = 1 का सत्यापन। त्रिकोणमितीय फलनों के संकेत। डोमेन, रेंज और ग्राफ। sin(x±y), cos(x±y) को sinx, cosx, siny, cosy के रूप में व्यक्त करना। sin2x, cos2x, tan2x, sin3x, cos3x और tan3x से संबंधित सूत्र।
सम्मिश्र संख्याएँ एवं द्विघात समीकरण
√–1 की आवश्यकता, विशेष रूप से द्विघात समीकरण हल करने में असमर्थता से प्रेरित। सम्मिश्र संख्याओं के बीजगणितीय गुण। आर्गेंड तल।
रैखिक असाम्यताएँ
रैखिक असाम्यताएँ, एक चर में असाम्यताओं के बीजगणितीय हल तथा संख्या रेखा पर उनका निरूपण।
क्रमचय और संचय
गणना का मूल सिद्धांत, फैक्टोरियल n (n!)। nPr और nCr के सूत्रों की व्युत्पत्ति और उनके उपयोग।
बाइनोमियल प्रमेय
ऐतिहासिक दृष्टिकोण, धनात्मक पूर्णांक घातांकों के लिए प्रमेय का कथन एवं प्रमाण। पास्कल त्रिभुज, सरल उपयोग।
अनुक्रम और श्रेणी
अनुक्रम और श्रेणी, अंकगणितीय अनुक्रम (A.P.), अंकगणितीय माध्य (A.M.), ज्यामितीय अनुक्रम (G.P.), सामान्य पद, n पदों का योग, अनंत G.P. और उसका योग, ज्यामितीय माध्य (G.M.), A.M. और G.M. के बीच संबंध।
सरल रेखाएँ
रेखा का ढाल और दो रेखाओं के बीच कोण। विभिन्न प्रकार की रेखाओं के समीकरण—धुरी के समानांतर, बिंदु-ढाल रूप, ढाल-अवरोध रूप। किसी रेखा से बिंदु की दूरी।
शंकव क्रियाएँ
शंकु के खंड—वृत्त, दीर्घवृत्त, परवलय, अधिवृत्त, बिंदु, सरल रेखा और दो प्रतिच्छेद रेखाएँ। मानक समीकरण एवं सरल गुण। परवलय, दीर्घवृत्त और अधिवृत्त के मानक समीकरण। वृत्त का मानक समीकरण।
त्रिविमीय ज्यामिति का परिचय
त्रिविमीय निर्देश अक्ष एवं तल। बिंदु के निर्देशांक। दो बिंदुओं के बीच दूरी।
सीमाएँ और अवकलज
गति परिवर्तन के रूप में अवकलज की अवधारणा, ग्राफ द्वारा व्याख्या। सीमाओं की अवधारणा—बहुपद, घातांक, त्रिकोणमितीय और लॉगरिदमिक फलनों की सीमाएँ। अवकलज की परिभाषा, रेखा की स्पर्शरेखा से संबंध। फलनों के योग, अंतर, गुणन एवं भाजन के अवकलज। बहुपद एवं त्रिकोणमितीय फलनों के अवकलज।
सांख्यिकी
विचलन के माप: परास, माध्य विचलन, विचरण एवं मानक विचलन (असमूहित / समूहित डेटा)।
प्रायिकता
यादृच्छिक प्रयोग; परिणाम, सैम्पल स्पेस। घटनाएँ: ‘नहीं’, ‘और’, ‘या’, परस्पर बहिष्कृत घटनाएँ, समावेशी घटनाएँ, सेट सिद्धांत पर आधारित स्वाक्षरिक प्रायिकता। अन्य कक्षाओं से संबंध।
संबंध एवं फलन (उन्नत)
रिफ्लेक्सिव, सिमेट्रिक, ट्रांजिटिव और समतुल्य संबंध। एक-एक और onto फलन।
व्युत्क्रम त्रिकोणमितीय फलन
परिभाषा, क्षेत्र, डोमेन, प्रमुख मूल्य शाखा। ग्राफ।
आव्यूह
परिकल्पना, संकेतांकन, क्रम, समानता, आव्यूह के प्रकार, शून्य एवं एकक आव्यूह, स्थानांतरण, सममित एवं विषम सममित आव्यूह। जोड़, गुणा एवं स्केलर गुणा। गुणों का अध्ययन। 2×2 के लिए शून्य गुणनफल वाले आव्यूह का अस्तित्व। उलटनीय आव्यूह और उसकी विशिष्टता का प्रमाण।
सारणिक
3×3 तक के वर्ग आव्यूह का सारणिक, माइनर, को-फैक्टर, त्रिभुज के क्षेत्रफल में उपयोग। सहगामी और व्युत्क्रमी आव्यूह। रैखिक समीकरणों की संगतता, असंगतता एवं हलों की संख्या, आव्यूह की सहायता से हल।
सततता और अवकलनीयता
सततता और अवकलनीयता, यौगिक फलनों के अवकलज, चेन नियम, व्युत्क्रम त्रिकोणमितीय, अन्तर्निहित, घातांक और लॉगरिदमिक फलनों के अवकलज। लॉगरिदमिक अवकलन, पैरामीट्रिक फलनों के अवकलज। द्वितीय अवकलज।
अवकलजों के अनुप्रयोग
गति परिवर्तन, बढ़ते/घटते फलन, अधिकतम-न्यूनतम (भौमितीय प्रेरणा और द्वितीय परीक्षण)। वास्तविक जीवन से जुड़ी समस्याओं पर आधारित प्रश्न।
समाकलन
अवकलन की प्रतिक्रिया के रूप में समाकलन। प्रतिस्थापन, आंशिक भिन्न एवं भागों द्वारा समाकलन। सरल समाकलनों का मूल्यांकन। निम्नलिखित प्रकार के सरल समाकलनों का मूल्यांकन एवं उन पर आधारित समस्याएँ।
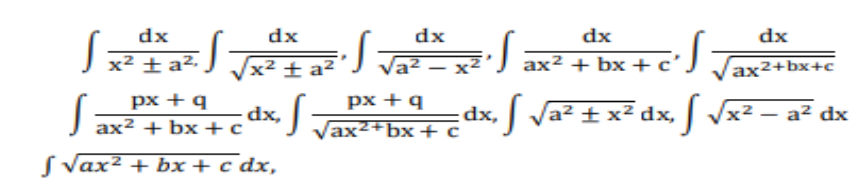
परिकलन का मूल प्रमेय। निश्चित समाकलनों के गुण।
समाकलनों के अनुप्रयोग
सरल वक्रों (रेखाएँ, वृत्त, परवलय, दीर्घवृत्त) के अंतर्गत क्षेत्रफल का निर्धारण।
अवकल समीकरण
परिभाषा, कोटि एवं घात, सामान्य एवं विशिष्ट हल। चर पृथक्करण विधि, समजात अवकल समीकरण। प्रथम कोटि के रैखिक अवकल समीकरण: dy/dx + py = q तथा dx/dy + px = q।
सदिश
सदिश एवं अदिश, परिमाण और दिशा। दिशा कोसाइन और अनुपात। समान, शून्य, एकात्मक, समांतर, सहरेखीय सदिश। बिंदु का स्थिति सदिश। सदिशों का जोड़, स्केलर गुणन, खंड विभाजन। स्केलर (डॉट) गुणन और सदिश (क्रॉस) गुणन की व्याख्या एवं उपयोग।
त्रिविमीय ज्यामिति
दो बिंदुओं को जोड़ने वाली रेखा के दिशा अनुपात और कोसाइन। रेखा का कार्तीय और सदिश समीकरण। विकर्ण रेखाएँ, न्यूनतम दूरी, दो रेखाओं के बीच कोण।
रैखिक प्रोग्रामन
परिचय, बाधाएँ, उद्देश्य फलन, इष्टतम समाधान, ग्राफ द्वारा हल, सीमा क्षेत्र, यथार्थ व अयथार्थ समाधान, इष्टतम समाधान।
प्रायिकता (उन्नत)
सशर्त प्रायिकता, गुणा प्रमेय, स्वतंत्र घटनाएँ, कुल प्रायिकता, बेयेस प्रमेय, यादृच्छिक चर, प्रायिकता वितरण, माध्य।

